

This formula is fundamental to understanding the concept and ensuring that each element in the population has an equal chance of being included in the sample. Simple random sampling relies on a straightforward formula to calculate the probability of selecting any particular member from a population. This methodological rigor enhances the reliability and validity of your research. If you need to conduct additional research or want to validate your findings, you can repeat the simple random sampling process to draw new samples.īy following these methods and steps, you can implement simple random sampling effectively, ensuring that your sample is both random and representative of the larger population. Remember that the results should be generalized to the entire population, as simple random sampling ensures representativeness. Analyze and Draw ConclusionsĪnalyze the data collected from your sample and draw conclusions or insights. This data will be the basis of your research or analysis. Once you have the list of selected sample members, notify them if necessary and collect the relevant data or responses. Ensure that the selection is truly random, with every member having an equal chance of being chosen. Select Sample Membersīased on the randomization method chosen, select the specified number of members from the population list.
Advantages and disadvantages of simple random sampling software#
Random Sampling Software: Utilize specialized software designed for random sampling. Randomization Tables: Create tables with random starting points and systematically choose members. Random Number Generators: Use software or tools that generate random numbers to select sample members. Use a Randomization MethodĮmploy a reliable randomization method to select the sample.
The sample size should be large enough to be statistically significant but manageable for data collection. Determine Sample Sizeĭecide on the desired sample size, which represents the number of individuals or items you want to include in your sample. This step ensures that each member can be easily distinguished in the sampling process. If the members of the population do not already have unique identifiers, assign each one a unique label or number. Each member should have a unique identifier, such as a numerical ID or a name. List All Population MembersĬreate a comprehensive list or database of all members of the population. This could be a group of individuals, items, or data points that you want to draw a sample from. Here’s a concise method overview.īegin by clearly defining the population you want to study. By following a systematic approach, you can achieve randomness and representativeness in your sample. Simple random sampling is a foundational technique in research and statistics, designed to ensure that each member of a population has an equal and independent chance of being selected for a sample.
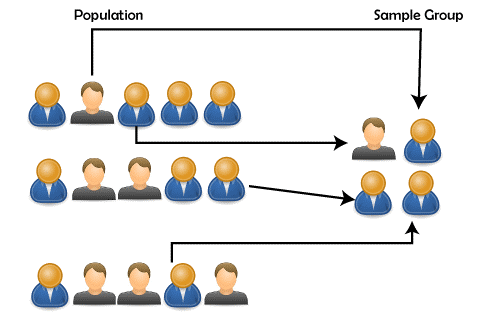
Simple random sampling is usually used for large populations, hence, it is important to ensure a sample size that is large enough to fittingly represent this population otherwise it will lead to an increase in margin of error. In other words, this method of sampling ensures that the data extracted from the chosen sample group is reflective of what it would be for the target population as a whole. This method of sampling is most apt for when the main objective of a study is for its findings to be generalizable for a whole population. Simple random sampling assigns numbers to everyone within the population, so that a sample group may be selected using processes that pick random numbers from the list. This means that when employed, simple random sampling gives everyone in the target population an equal and known probability of being selected as a respondent in the sample group. Simple random sampling is a sampling method used in market research studies that falls under the category of probability sampling.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
